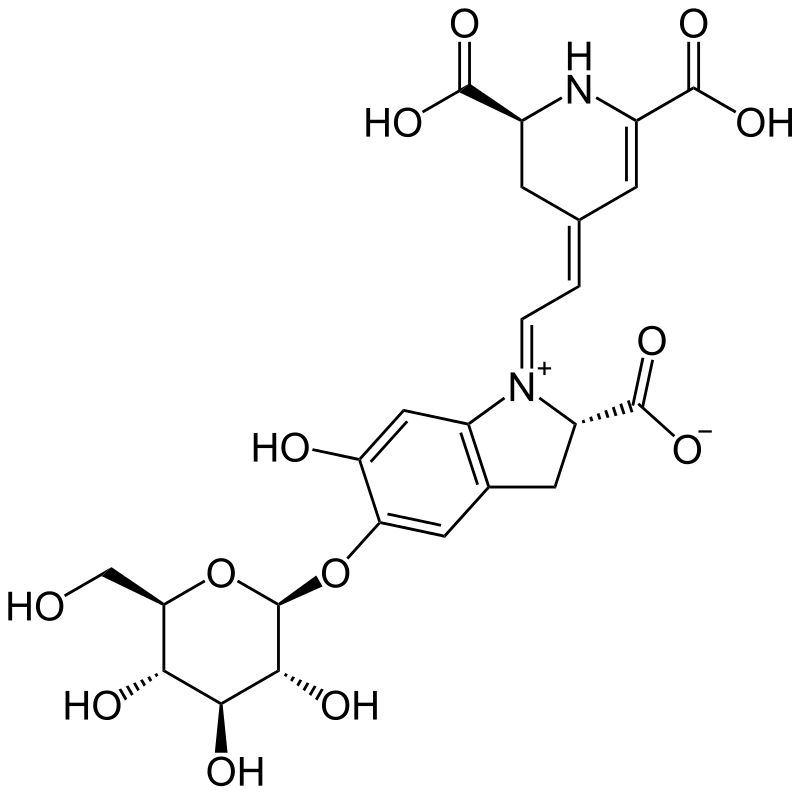
Description
Names
IUPAC name
4-(2-(2-carboxy-5-(beta-D-glucopyranosyloxy)-2,3-dihydro-6- hydroxy-1H-indol-1-yl)ethenyl)-2,3-dihydro-(S-(R*,R*))-2,6-pyridinedicarboxylic acid
Identifiers
CAS Number · 7659-95-2
3D model (JSmol) · Interactive image
ChEBI · CHEBI:3080
ChEMBL · ChEMBL1172614
ChemSpider · 10128200
ECHA InfoCard 100.028.753
E number E162 (colours)
KEGG · C08540
PubChem CID · 12300103
Properties
Chemical formula C24H26N2O13
Molar mass 550.47 g/mol
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
What is the difference between a dye and a pigment?
Pigments
There are two different types of pigments: Natural and Synthetic. Pigments are insoluble materials that are ground into a fine powder so that they can be suspended in a binder (usually an oil). Insolubility means that pigments can never be dissolved into the binder, the fine particles of the powder are suspended and stay solid in the binder. The binder surrounds the pigment particles and holds them in place.
Pigments produce paints that are more opaque than dyes and have low tinting strength. Opacity is the ability for paint to cover and hide another dried color that it has been applied over. Tinting strength is how well a color mixes with other colors. (Example: When mixing blue with white, how well does the blue disperse into the white? or How blue does the white look after the mixing?)
The first colorants that were used to create paint were naturally occuring earthen pigments. Prehistoric people used ochres and iron oxides to create images on cave walls in Lascaux, France. Many natural insoluble pigments are still used today in artists’ paints. Metals are also natural insoluble pigments, like cadmium, titanium, and lead (very toxic).
Dyes
There two types of dyes: Natural and Synthetic. Dyes, in contrast to pigments, are soluble colorants. Solubility means that dyes are dissolved into a binder (usually water). Dyes are more transparent than pigments. Transparency of dyes makes these colors very good for glazing over previous layers of paint. Dyes have high tinting strength. A dye based paint, like pthalo blue, concentrates its own color when mixed with another color of paint, like titanium white.
Dyes originally were derived from natural sources. Plants were primarily used to get dyes. Today some dyes are still organic, but many are created from synthetic materials. Indian Yellow is a good example of why synthetic dyes have replaced some naturally derived colors. The original Indian Yellow was made from dried elephant urine, but now it is considered inhumane to force an healthy diet onto an animal in order to influence the color of their urine. Today’s Indian Yellow is made from a synthetic dye.
Please note that if you purchase a dye, it may come in either granular or powder form, depending on availability. We provide the granular for wherever possible, as it is easier to handle and produces less airborne dust.